The Centre for Advanced Research in Environmental Radioactivity (CARER) at Mangalore University has initiated a series of International Intercomparison Experiments focused on radon measuring devices, starting on October 30, 2025. This month-long program aims to improve the accuracy and global standards of radon measurement in Mangaluru.
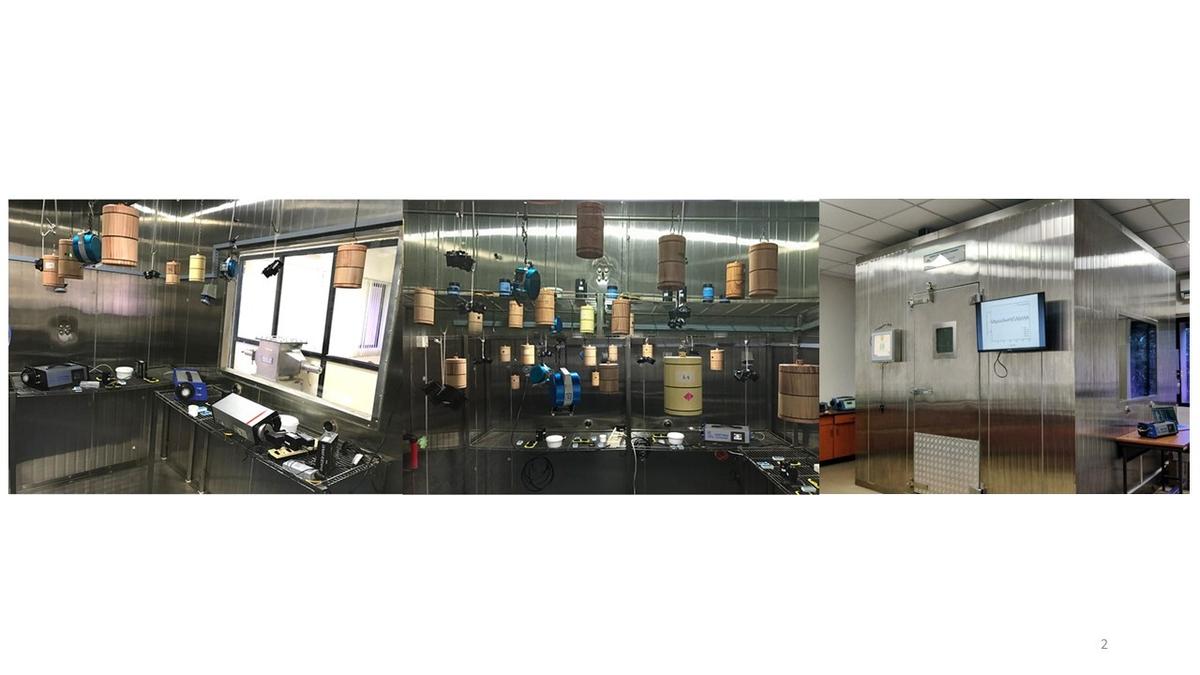
Utilizing the advanced Radon Calibration Facility at CARER, which is recognized as the largest and most sophisticated facility of its kind in Asia, the experiments will involve collaboration with entities such as the Asian and Oceanic Radon Association (AORA) and the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) based in Mumbai. Laboratories from various countries, including Japan, Australia, Spain, Sweden, the United States, the United Kingdom, and India, will participate in this initiative.
Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, significantly contributes to indoor radiation exposure, accounting for approximately 50% of the overall natural background radiation dose, which is about 2.4 milli Sievert per year. The intercomparison will involve around 300 radon detectors that will be tested and evaluated under controlled environmental conditions. CARER”s proprietary technologies will facilitate this performance evaluation.
The goal of these intercomparison experiments is to ensure the precision and reliability of radon measurements, facilitating global harmonization. This initiative is a crucial step in refining international standards and enhancing the understanding of radiological risks associated with radon exposure.
Radon originates from the decay of uranium found in soil, rock, and building materials, and can accumulate in enclosed environments like homes and offices. While the risk posed by radon is notably higher in temperate regions, the tropical climate of India, along with well-ventilated living spaces, typically results in lower indoor radon levels.
According to Karunakara Naregundi, the Centre Coordinator, “Advanced radon detectors — including RAD7, RAD8, RADUET, ARP monitors, DRPS, Eurofins alpha-track devices, Pinhole dosimeters, Smart RnDuo, and Alphaguard — from leading international laboratories will be evaluated during this exercise.”
Established in 2015 with support from the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences (BRNS) and technical expertise from BARC, CARER has emerged as the largest center for radiation protection studies in Asia and is recognized as the second-largest globally.