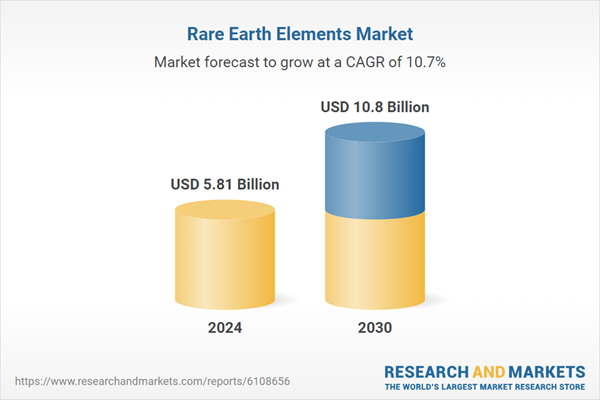
The global market for rare earth elements (REE) is poised for substantial growth, with projections indicating an increase from USD 5.81 billion in 2024 to USD 10.80 billion by 2030. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.72%. The insights are detailed in a new report titled “Rare Earth Elements Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, 2020-2030F,” recently released by ResearchAndMarkets.com.
Rare earth elements consist of 17 chemically similar metallic elements, including lanthanides, scandium, and yttrium. These materials are essential for various high-tech applications across multiple sectors, including clean energy, electronics, defense, and automotive industries. Their significance is particularly pronounced in the production of high-performance magnets utilized in electric vehicles (EVs), wind turbines, smartphones, aerospace systems, and fiber optics, which are critical for advancing innovation and sustainability.
Demand Surge in Clean Energy and Electric Vehicles
The escalating demand for rare earth elements is largely driven by the global transition towards clean energy and the electrification of transportation. These elements are crucial for crafting high-performance permanent magnets that power wind turbines and electric motors. Key components such as neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium are particularly vital for traction motors in EVs and direct-drive generators used in wind energy systems. With the rapid development of wind energy projects and a significant increase in electric vehicle manufacturing, the demand for rare earth-based magnets is experiencing remarkable growth. Their efficiency, compactness, and durability are indispensable for achieving international decarbonization and net-zero targets.
Challenges Facing the Rare Earth Sector
Despite the opportunities, the rare earth elements market faces significant challenges, primarily stemming from geopolitical dependencies and supply chain vulnerabilities. A large proportion of the world”s REE mining and refining is concentrated in a few countries, notably China. This concentration heightens the industry”s exposure to geopolitical and trade-related risks. Any disruptions resulting from export restrictions, diplomatic conflicts, or regulatory shifts could lead to shortages and market instability. These risks create uncertainty for manufacturers who rely on rare earths for essential technologies across energy, defense, and communication sectors, prompting a growing call for supply chain diversification and the bolstering of domestic production capabilities.
Trends Shaping the Future of Rare Earth Elements
A notable trend in the REE market is the increasing integration of rare earth magnets into renewable energy systems and electric vehicles. As nations amplify their wind energy capacities and embrace electric mobility, the demand for rare earth elements such as neodymium and dysprosium continues to rise. These materials are crucial for lightweight, robust magnets that are integral to high-torque motors and efficient turbine generators. The reliance on these elements in next-generation electric vehicle platforms and offshore wind farms is driving investment in rare earth extraction, refining, and magnet production, especially in regions aiming for energy independence and technological resilience.
Key players in the rare earth elements market include China Northern Rare Earth Group High-Tech Co., Ltd., Lynas Rare Earths Ltd., MP Materials Corp., and Arafura Rare Earths Limited, among others. The market is segmented by type, application, and region, covering diverse uses from magnets and batteries to catalysts and polishing agents.