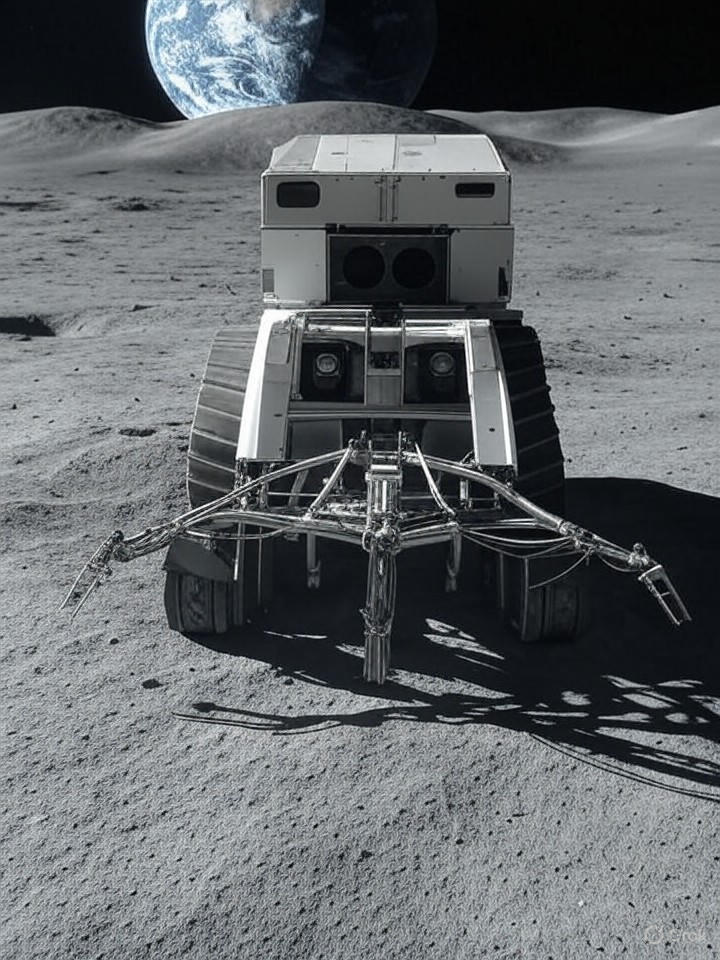
Interlune, a forward-thinking mining company, has recently announced the discovery of helium-3 deposits on the Moon. This rare isotope, valued at up to $20 million per kilogram, is critical for applications ranging from fusion energy to quantum computing and medical technologies. The announcement highlights the increasing interest in space mining as nations and private ventures strive to exploit the Moon”s untapped resources.
Utilizing advanced surveying techniques, Interlune asserts that it has accurately identified these valuable reserves, paving the way for what could be the first commercial extraction of lunar materials. Helium-3 is particularly sought after due to its abundance in lunar regolith, a result of exposure to solar wind over billions of years. Unlike the more commonly found helium-4, helium-3 is non-radioactive and presents a significant opportunity for nuclear fusion, which could lead to a sustainable and waste-free energy source.
The announcement comes amid a climate of heightened competition among global powers, with the United States, China, and Russia all vying for dominance in lunar exploration and resource extraction. According to reports, Interlune”s initiatives are in line with broader goals to secure helium-3 for quantum computing, where it serves as an essential coolant for ultra-low temperature operations.
Interlune has already made strides in establishing partnerships, including an agreement to provide up to 10,000 liters of extracted helium-3, illustrating early confidence in the market. The company has also revealed a prototype harvester capable of processing 110 tons of lunar soil per hour, addressing the complex logistical challenges posed by lunar operations, including extreme temperatures and the lack of an atmosphere, while striving to minimize environmental impact.
The potential applications of helium-3 extend beyond energy, impacting fields such as medical imaging and supercomputing. Reports indicate that Interlune is developing autonomous robotic systems for mining, which could be operational by 2028, coinciding with NASA”s Artemis program and China”s Chang”e missions. These initiatives may provide the necessary infrastructure for the transportation and processing of lunar materials.
Despite the promise of lunar resource extraction, challenges remain, particularly the high costs associated with space travel and the uncertain economics of returning materials to Earth. Proponents argue that in-situ resource utilization—utilizing lunar resources to build habitats or fuel stations—could help mitigate these costs. The race for helium-3 has been likened to “moon gold,” and the involvement of global superpowers, including Russia, could significantly alter the landscape of energy geopolitics.
Financially, the venture has garnered attention from investors, with Interlune securing funding to deploy multispectral cameras for accurate resource mapping. A notable partnership with a quantum cryogenics company, Bluefors, has resulted in one of the largest contracts in the space resources sector, highlighting the high demand for helium-3 in advancing computational technologies.
Ethically, the endeavor raises questions about fair access to lunar resources under the Outer Space Treaty. Critics warn of a potential new colonial rush for the Moon”s riches, while supporters argue that shared technological advancements, such as safer fusion energy, could provide solutions to climate change challenges.
Looking forward, successful helium-3 extraction could catalyze a wider space economy, opening avenues for the extraction of water ice, rare earth elements, and oxygen from lunar soil. Insights suggest that such developments could facilitate permanent lunar settlements, thereby lessening Earth”s resource dependency. For industry stakeholders, the scalability of Interlune”s prototypes will be crucial, as successful operations could attract substantial investments, transforming space exploration from a scientific endeavor into a lucrative industry.
Ultimately, this lunar initiative signifies a critical transformation, where the Moon”s surface emerges as a site for innovation and commerce. As extraction technologies advance, the vision of harnessing cosmic resources moves closer to realization, promising significant impacts on Earth”s technological landscape.