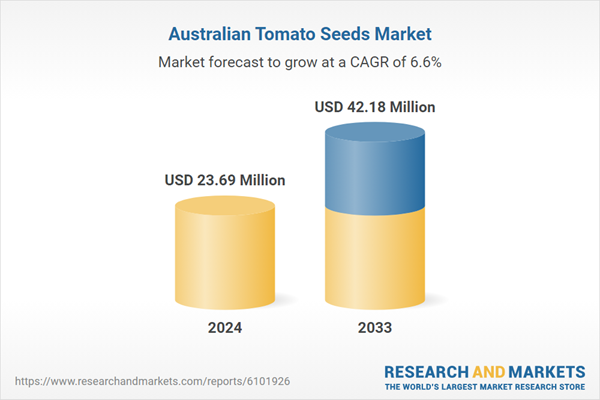
Australia”s tomato seeds market is anticipated to experience substantial growth, reaching approximately USD 42.18 million by 2033, up from USD 23.69 million in 2024. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.62% from 2025 to 2033, according to a report by ResearchAndMarkets.com.
The expansion of the market is attributed to several factors, including a rise in greenhouse farming, an increasing preference for locally sourced produce, and advancements in seed breeding technology. The diverse climate zones across Australia are contributing to the demand for various seed types, particularly hybrid and disease-resistant varieties.
Drivers of Market Growth
One of the primary factors propelling the growth of the tomato seeds market is the significant rise in greenhouse production. This method allows for year-round cultivation by providing a controlled environment that mitigates the challenges posed by seasonal weather fluctuations. Greenhouses enable consistent crop yields and high-quality produce by regulating temperature, humidity, and light. Furthermore, tomatoes grown in greenhouses are less vulnerable to pests and diseases, enhancing plant health and reducing the need for chemical treatments, which promotes sustainability.
Another key driver is the growing consumer demand for locally grown and organic produce. In Australia, tomatoes are particularly favored, as fresh, locally sourced food is perceived as healthier and more environmentally friendly. This shift in consumer behavior encourages farmers to adopt agricultural practices that align with these preferences, such as organic farming and sustainable growing techniques. Consequently, there is a heightened need for tomato seed varieties that thrive under local growing conditions and are suited for organic agriculture, fostering innovation within the seed sector.
Technological Innovations in Seed Breeding
Recent advancements in seed breeding technology have played a crucial role in shaping the Australian tomato seed market. Innovations such as genetic modification and marker-assisted selection have enabled the development of tomato seed varieties with enhanced characteristics, including improved disease resistance, greater yield potential, and better adaptability to varying climatic conditions. These technological improvements allow farmers to cultivate tomatoes that are more resilient to environmental stressors, thereby reducing reliance on chemical treatments and improving overall crop health.
Challenges Facing the Market
Despite its growth prospects, the Australian tomato seeds market faces several challenges. Climate variability and extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, pose significant threats to the agricultural sector. Tomatoes are particularly sensitive to environmental changes, and unpredictable weather can adversely affect crop yields, hinder plant growth, and lower seed germination rates. As a result, there is an increasing necessity for climate-resilient seed varieties that can withstand harsh conditions, although these advanced seeds often come at a higher cost, which can be a barrier for many farmers.
Additionally, the high price of high-quality seeds, which are essential for boosting productivity in tomato farming, poses a considerable challenge, particularly for small-scale or independent farmers. Many of these producers may resort to reusing seeds from previous crops or opting for cheaper, lower-quality alternatives, leading to diminished yields and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. The financial burden of investing in superior seeds can limit experimentation with new varieties and hinder overall market growth.
The report outlines a comprehensive analysis of the Australian tomato seeds market, including historical trends, market forecasts, and an overview of key players such as BASF S.E., Sakata Seed Corporation, and Bayer Crop Science SE.
For more detailed insights, the full report is available on ResearchAndMarkets.com.