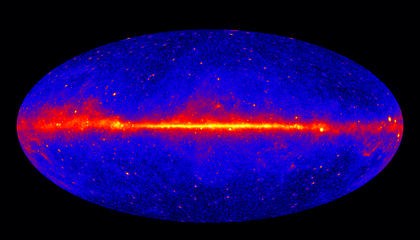
A recent analysis of gamma rays emanating from the center of the Milky Way has raised intriguing questions regarding the existence of dark matter. Researchers have observed an unexpected excess of these high-energy rays, which could potentially signify the presence of dark matter particles.
Dark matter, an elusive and largely theoretical form of matter, is believed to make up a significant portion of the universe”s total mass. Its effects are inferred through gravitational interactions rather than direct detection, as it does not emit light.
The gamma rays in question appear to be concentrated in a region known for its mysterious properties, where the gravitational pull is strong and complex interactions are at play. Some scientists argue that this increase in gamma rays could be evidence of dark matter annihilation, a process theorized to occur when dark matter particles collide and annihilate each other, producing gamma rays as a byproduct.
However, the interpretation of this data is not straightforward. While the gamma rays may suggest dark matter activity, alternative explanations exist. For instance, they could originate from known astrophysical sources, such as pulsars or supernova remnants, rather than being linked to dark matter.
The ongoing debate highlights the challenges that astrophysicists face in unraveling the mysteries of dark matter. Researchers continue to analyze the gamma ray emissions, seeking to determine their origins and implications for our understanding of the universe.
This inquiry into the Milky Way”s center not only aims to clarify the nature of dark matter but also contributes to the broader quest to understand the cosmos and its fundamental components. As more data becomes available, scientists hope to shed light on this enigmatic subject, potentially leading to groundbreaking discoveries about the fabric of our universe.