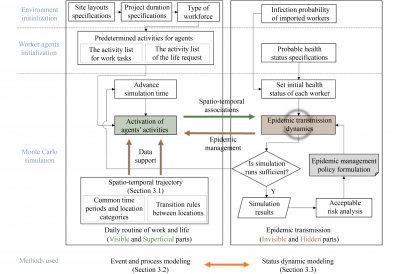
Sudden pandemics present significant challenges in the management of construction sites, threatening both worker health and the timeline of projects. The nature of construction work, which often requires intense labor and close physical interactions among workers, increases the risk of infection, leading to delays, increased costs, and a decline in project quality.
Existing studies primarily focus on the statistical analysis of the negative impacts of pandemics on the construction industry. However, there is a notable lack of research dedicated to developing adaptive management strategies tailored specifically for construction sites. Conventional methods of post-causal inference, such as archival analysis and surveys, fail to deliver insights that are specific to various scenarios or provide counterfactual analyses.
Traditional epidemic simulation models, which rely on contact lists, are generally not suitable for the unique characteristics of construction sites. These sites often feature semi-open outdoor environments and distinct patterns of worker movement, complicating standard approaches to epidemic modeling.
To address these issues, the application of agent-based modeling presents a promising solution. This approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of how pandemics can impact construction operations and enables the development of effective, scenario-specific management strategies. By simulating various pandemic scenarios, stakeholders can better prepare and respond to the challenges posed by infectious diseases.
In conclusion, the construction industry must pivot towards adaptive management strategies that are informed by advanced modeling techniques to safeguard worker health and maintain project integrity during pandemics.